Have you ever thought about how search engines find exactly what you’re looking for? They usually use a mix of matching specific words and understanding the meaning behind them. This is called hybrid search. Now, let’s build a simple document retrieval flow that combines both approaches.
Understanding BM25
BM25 is a ranking algorithm used in information retrieval systems to estimate the relevance of documents to a given search query.
- What it does: It looks at how often your search words appear in a document and considers the document length to provide the most relevant results.
- Why it’s useful: It’s perfect for sorting through huge collections of documents, like a digital library, without bias towards longer documents or overused words.
Key elements of BM25
- Term Frequency (TF): This counts how many times your search terms appear in a document.
- Inverse Document Frequency (IDF): This gives more importance to rare terms, making sure common words don’t dominate.
- Document Length Normalization: This ensures longer documents don’t unfairly dominate the results.
- Query Term Saturation: This stops excessively repeated terms from skewing the results.
Overall, the score is:
score(d, q) = ∑(tf(i, d) * idf(i) * (k1 + 1)) / (tf(i, d) + k1 * (1 - b + b * (dl / avgdl)))When is BM25 (keyword search) ideal?
- Large Document Collections: Perfect for big databases where you need to sort through lots of information.
- Preventing Bias: Great for balancing term frequency and document length.
- General Information Retrieval: Useful in various search scenarios, offering a mix of simplicity and effectiveness.
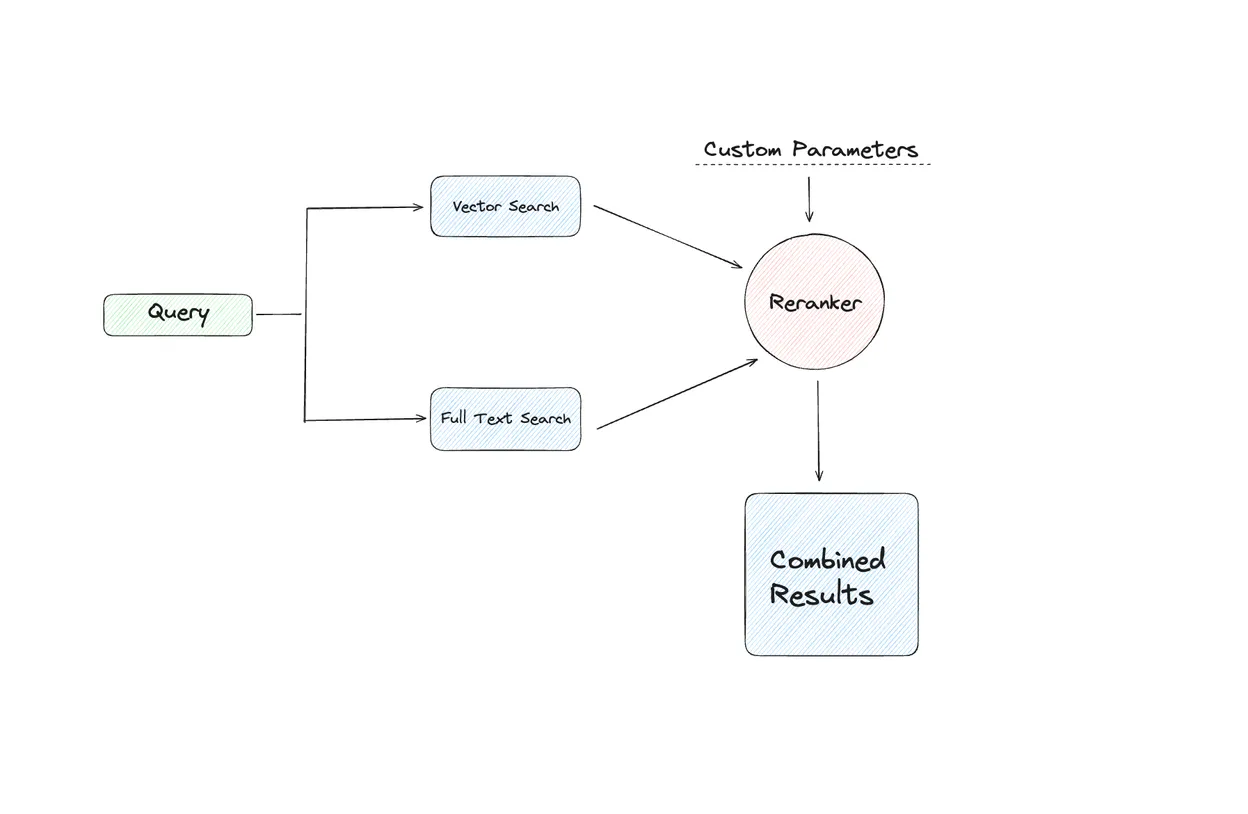
Practical Application: Building a Hybrid Search System
Imagine you’re crafting a search system for a large digital library. You want it not only to find documents with specific keywords but also to grasp the context and semantics behind each query. Here’s how:
- Step 1: BM25 quickly fetches documents with the search keywords.
- Step 2: A vector database (VectorDB) digs deeper to find contextually related documents.
- Step 3: An ensemble retriever runs both systems, combines their results, and reranks them to present a more complete set of documents to the user.
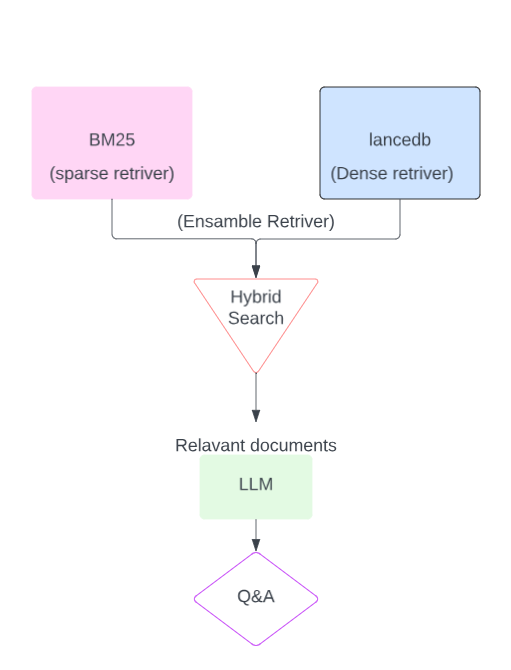
What Exactly is Hybrid Search?
Hybrid search is a two-pronged approach that combines lexical matching with semantic similarity:
- Keyword Search: This is the age-old method we’re most familiar with. Input a word or a phrase, and this search hones in on those exact terms or closely related ones in the database or document collection.
- Vector Search: Vector search goes beyond exact terms by using embeddings to capture meaning. Even if a document doesn’t contain the same words, it can still be retrieved if the underlying meaning is similar.
Follow along with the Colab notebook:
Let’s get to the code. Here we’ll use LangChain with a LanceDB vector store.
# example of using BM25 & LanceDB - hybrid search
from langchain.vectorstores import LanceDB
import lancedb
from langchain.retrievers import BM25Retriever, EnsembleRetriever
from langchain.schema import Document
from langchain.embeddings.openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain.document_loaders import PyPDFLoader
# Initialize embeddings
embedding = OpenAIEmbeddings()Next, load a single PDF.
# load single pdf
loader = PyPDFLoader("/content/Food_and_Nutrition.pdf")
pages = loader.load_and_split()Create a BM25 sparse keyword-matching retriever:
# Initialize the BM25 retriever
bm25_retriever = BM25Retriever.from_documents(pages)
bm25_retriever.k = 2 # Retrieve top 2 resultsCreate a LanceDB vector store for dense semantic search/retrieval:
db = lancedb.connect('/tmp/lancedb')
table = db.create_table("pandas_docs", data=[
{"vector": embedding.embed_query("Hello World"), "text": "Hello World", "id": "1"}
], mode="overwrite")
# Initialize LanceDB retriever
docsearch = LanceDB.from_documents(pages, embedding, connection=table)
retriever_lancedb = docsearch.as_retriever(search_kwargs={"k": 2})Now combine both retrievers. You can tune the weighting based on how much you trust keyword vs. semantic matches:
# Initialize the ensemble retriever
ensemble_retriever = EnsembleRetriever(
retrievers=[bm25_retriever, retriever_lancedb],
weights=[0.4, 0.6],
)
# Example customer query
query = (
"Which foods help build strong bones and teeth?\n"
"Which vitamins and minerals are important for this?"
)
# Retrieve relevant documents/products
docs = ensemble_retriever.get_relevant_documents(query)With an ensemble retriever, LangChain performs keyword search (e.g., matching phrases like “strong bones” and “teeth”) and semantic search via LanceDB to find the most similar passages by embedding similarity.
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
llm = ChatOpenAI(openai_api_key="sk-yourapikey")
# if you want to use open source models such as Llama, Mistral see:
# https://github.com/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/tutorials/chatbot_using_Llama2_&_lanceDB
qa = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(llm=llm, chain_type="stuff", retriever=ensemble_retriever)
query = "what nutrition needed for pregnant women"
qa.run(query)Here, BM25 searches for keywords like “nutrition”, “pregnant”, and “women” while LanceDB retrieves semantically similar passages. Together, this often produces more useful context for answering the question.
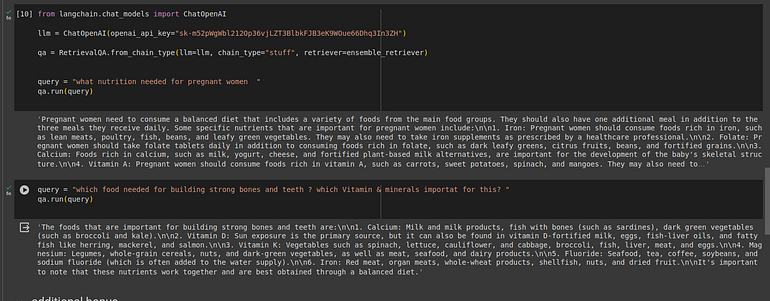
Below are answers from a traditional RAG setup. You can check this in our repo . Results may vary based on parameters, models, and prompts.
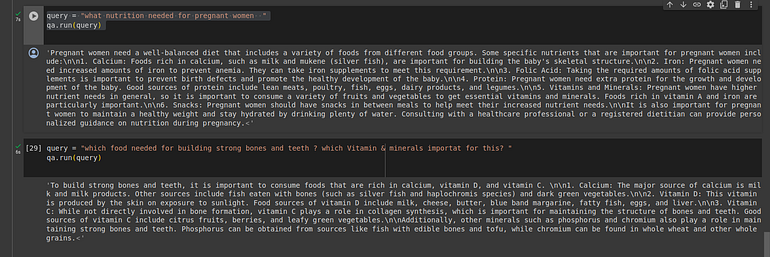
You can try this on Google Colab with your own PDF and use case. Hybrid search is a practical way to improve retrieval quality—especially when users mix precise keywords with broader intent.
Explore More with Our Resources
Discover the full potential of hybrid search (and more) in the LanceDB ecosystem. LanceDB is a setup-free, persistent vector database that scales to on-disk storage. For a deeper dive into applied GenAI and vector database examples and tutorials, see vectordb-recipes . From advanced RAG methods like FLARE, reranking, and HyDE to practical use cases, these resources are designed to inspire your next project.